Basic Usage
This section describes the basic usage of the configurator such as creating the environment for pre-defined Seco configurations and/or customize build environments. The section Advanced usage describe how to add configurations settings to the already existing ones and a deeper description on how the configurator works.
Configure Seco board with default settings
Find and select the configuration
To create a build environment for a Seco board with the default configuration requires very few steps. To list all Seco boards default configurations run:
yoctouser@acbeeb0d56d8:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -l
Configuration Description
-------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
qemuarm64_clea-os QEMU virt ARMv8 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
qemuarm_clea-os QEMU virt ARMv7 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
qemux86_64_clea-os QEMU x86-64 (q35) for Clea OS and default settings
qemux86_clea-os QEMU x86 (q35) for Clea OS and default settings
raspberrypi4_64_clea-os Raspberry Pi 4 for Clea OS FB and default settings
raspberrypi5_clea-os Raspberry Pi 5 for Clea OS FB and default settings
seco_intel_clea-os SECO HW based on INTEL chipsets for Clea OS FB and default settings
seco_sbc_c31_clea-os SBC RK3399 C31 board for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
seco_sbc_d23_clea-os SBC PX30 D23 board for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
seco_sbc_e09_clea-os SBC RK3568 E09 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
NOTE: this guide has been written during the development of CleaOS 2.0. Many other configurations will be added.
This command lists all the defconfigs in layers/base/configs. Whenever a new Seco board will be integrated in CleaOS it needs its own configuration there. When a custom layer is included, if it contains specific customized boards, the configurations will be shown. For example, assuming a custom layer called meta-seco-xyz with a custom board:
yoctouser@acbeeb0d56d8:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -l
***
INFO: Found custom layer "seco-xyz"!!! Use it.
***
Configuration Description
-------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
qemuarm64_clea-os QEMU virt ARMv8 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
qemuarm_clea-os QEMU virt ARMv7 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
qemux86_64_clea-os QEMU x86-64 (q35) for Clea OS and default settings
qemux86_clea-os QEMU x86 (q35) for Clea OS and default settings
raspberrypi4_64_clea-os Raspberry Pi 4 for Clea OS FB and default settings
raspberrypi5_clea-os Raspberry Pi 5 for Clea OS FB and default settings
seco_intel_clea-os SECO HW based on INTEL chipsets for Clea OS FB and default settings
seco_sbc_c31_clea-os SBC RK3399 C31 board for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
seco_sbc_d23_clea-os SBC PX30 D23 board for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
seco_sbc_e09_clea-os SBC RK3568 E09 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
seco_custom_xyz_clea-os Custom board for customer XYZ
Consider that the path of the custom defconfigs changes between CleaOS 1.0 and CleaOS 2.0 releases:
- for CleaOS 1.0 the configurator looks into the folder
layers/meta-seco-xyz/conf/configs - for CleaOS 2.0 the configurator looks into the folder
layers/meta-seco/meta-seco-xyz/conf/configs
NOTE: From now on it's assumed CleaOS 2.0 structure.
To select a configuration from the table, run:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -d <defconfig>
For example Seco's E09 board seco_sbc_e09_clea-os run:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -d seco_sbc_e09_clea-os
***
USE defconfig configuration file: seco_sbc_e09_clea-os
SBC RK3568 E09 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
***
This command creates in layers/base several files:
mconf: is the graphicalmenuconfig's binary. It's built the first time the command. ./seco-setup.sh -d <defconfig>is issued.conf: is the CLImenuconfig's binary. It's built the first time the command. ./seco-setup.sh -d <defconfig>is issued..config: is the result of the selected configuration processed byconfexecutable following theYconfigtree.seco-setup.log: is a log file containing debug messages printed by the configurator during the build environment creation process.
The content of .config is used by the configurator in the next step, when the build environment is actually created.
Create the build environment
With the .config generated it's possible to create the build environment running:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -c
For example:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -c
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-URL found in the configuration.
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-REALM found in the configuration.
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-PAIRING-TOKEN found in the configuration.
WARNING: no RAUC found in the configuration.
Welcome to SECO BSP
The Yocto Project has extensive documentation about OE including a
reference manual which can be found at:
http://yoctoproject.org/documentation
For more information about OpenEmbedded see their website:
http://www.openembedded.org/
Your build environment has been configured with:
MACHINE=seco-rk3568-e09
SDKMACHINE=i686
DISTRO=clea-os-fb
EULA=
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir/build_e09$
This command let the configurator process the .config in order to create the build environment. The results of this command are:
- creating environment variables configuring
bitbake. - creating the
builddirectory populated with aconffolder and a symbolic link to the build configurator.
Environment variables
The environment variables are created exploiting poky's built-in oe-init-build-env script. For example, for Seco E09 the environment differences are:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ diff env-pre-configurator env-post-configurator
0a1,3
> declare -x BBPATH="/home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09"
> declare -x BB_ENV_PASSTHROUGH_ADDITIONS="ALL_PROXY BBPATH_EXTRA BB_LOGCONFIG BB_NO_NETWORK BB_NUMBER_THREADS BB_SETSCENE_ENFORCE BB_SRCREV_POLICY DISTRO FTPS_PROXY FTP_PROXY GIT_PROXY_COMMAND HTTPS_PROXY HTTP_PROXY MACHINE NO_PROXY PARALLEL_MAKE SCREENDIR SDKMACHINE SOCKS5_PASSWD SOCKS5_USER SSH_AGENT_PID SSH_AUTH_SOCK STAMPS_DIR TCLIBC TCMODE all_proxy ftp_proxy ftps_proxy http_proxy https_proxy no_proxy "
> declare -x BUILDDIR="/home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09"
10,11c13,15
< declare -x OLDPWD="/home/yoctouser/workdir"
< declare -x PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
---
> declare -x OE_ADDED_PATHS="/home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/poky/scripts:/home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/poky/bitbake/bin:"
> declare -x OLDPWD="/home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09"
> declare -x PATH="/home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/poky/scripts:/home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/poky/bitbake/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin:/home/yoctouser/workdir"
12a17
> declare -x PYTHONPATH="/home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/poky/bitbake/lib:"
where env-pre-configurator and env-post-configurator are files created redirecting the output of export before and after running the configurator.
Build directory - Physical Seco board
When running the configurator with the -c flag, after the configurator succeeded, it automatically changes directory to the build folder. For example, building for the Seco E09 based on Rockchip processor, the resulting build directory has the following content:
$ tree -a build_e09/
build_e09/
├── conf
�│ ├── bblayers.conf
│ ├── .config
│ ├── conf-notes.txt
│ ├── conf-summary.txt
│ ├── local.conf
│ ├── local.conf.sample
│ ├── SRCREV.conf
│ └── templateconf.cfg
└── seco-setup.sh -> /home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/base/seco-setup.sh
The most relevants files are:
conf/bblayers.conflists paths to the directories containing metadata layers (e.g., meta, meta-poky, meta-seco) that provide recipes, classes, and configurations for building the image.conf/local.confis the primary configuration file for customizing the build environment and for defining variables use throuhgout the project. This file contains the critical variables (such asDISTRO,MACHINE, ect.) for correctly building an image.conf/SRCREV.confmanages the source revision control settings for recipes that fetch source code from version control systems. This file simplifies the management of SRCREV variables, which define the specific commit or revision of the source code to use for a given recipe.conf/.configis a copy oflayers/base/.configcreated in the previous step.conf/local.conf.sampleis the original file generated by poky's scriptoe-init-build-env. This file is used by the configurator to check if a build directory is a proper Yocto build directory.
How these files are populated is discussed in this section.
Build directory - Non-Seco boards
For non-Seco boards the procedure is the same. The content of the build directory for QEMU ARM64 (qemuarm64_clea-os) is the following:
$ tree -a build_qemuarm64/
build_qemuarm64/
├── conf
│ ├── bblayers.conf
│ ├── .config
│ ├── conf-notes.txt
│ ├── conf-summary.txt
│ ├── local.conf
│ ├── local.conf.sample
│ └── templateconf.cfg
└── seco-setup.sh -> /home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/base/seco-setup.sh
The difference in the files tree is that for the non-Seco boards the file conf/SRCREV.conf is not created.
Setup already existing build environment
If there is an already existing build directory created with the configurator, it can be used to re-create the build environment with:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh <build_directory>
For example:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh build_e09
Welcome to SECO BSP
The Yocto Project has extensive documentation about OE including a
reference manual which can be found at:
http://yoctoproject.org/documentation
For more information about OpenEmbedded see their website:
http://www.openembedded.org/
Your configuration files at /home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09 have not been touched.
Build
Within the build directory run bitbake <image> to build the image.
Customize build settings
Create a configuration from scratch
To start-off creating a configuration for a Seco board (i.e. the file layers/base/.config does not exist) graphically, run the configurator with the flag -m:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -m
***
SECO provides a menuconfig interfaces to create new Yocto project.
Please set the wanted configuration and save it.
Through this menu you can select:
- machine e distro
- Yocto's project parameters
- HW specific configuration
- Cloud connection setting
***
config/Yconfig/Yconfig_machine:5: can't open file "../meta-seco/meta-/conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_machine"
config/Yconfig/Yconfig_distro:4: can't open file "../meta-seco/meta-/conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_distro"
A menuconfig instance is opened in the current terminal looking like follows:
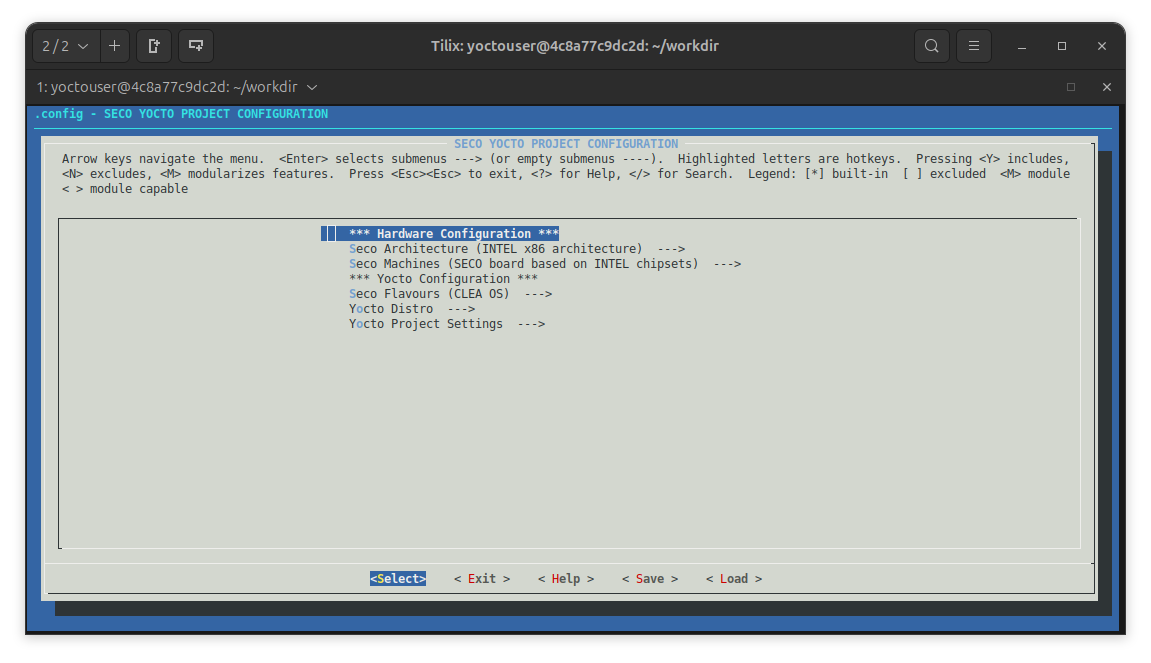
After the configuration has been changed and saved the layers/base/.config file is created. Then to create a build directory with the custom configuration regularly run . ./seco-setup.sh -c.
The warning strings:
config/Yconfig/Yconfig_machine:5: can't open file "../meta-seco/meta-/conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_machine"
config/Yconfig/Yconfig_distro:4: can't open file "../meta-seco/meta-/conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_distro"
shown when running the configurator with -m are caused by the absence of a custom layer. With a custom layer containing conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_machine and conf/Yconfig/Yconfig_distro the warning disappears. In those file can be added custom specific Yconfig entries.
Modify a preset configuration
It's possible to create a custom configuration starting from an already existing defconfig. For example, to customize a build based on Seco E09 board, firstly create the initial layers/base/.config file with:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -d seco_sbc_e09_clea-os
***
USE defconfig configuration file: seco_sbc_e09_clea-os
SBC RK3568 E09 for Clea OS Wayland and default settings
***
Enter into the graphical menuconfig with:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -m
to land to the main menu:
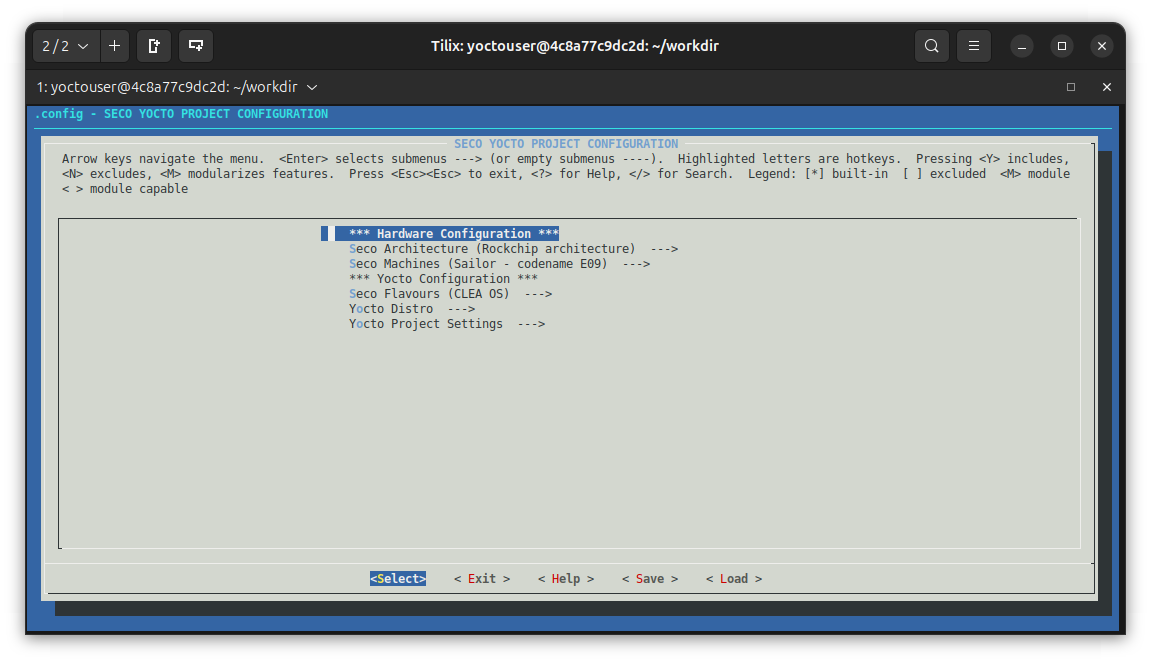
Now, customize the configuration graphically. For example, changing the build directory name to build_e09_customized and adding INHERIT += "rm_work" to local.conf. To do that, navigate to the Yocto Project Settings menu and switch from the default configuration:
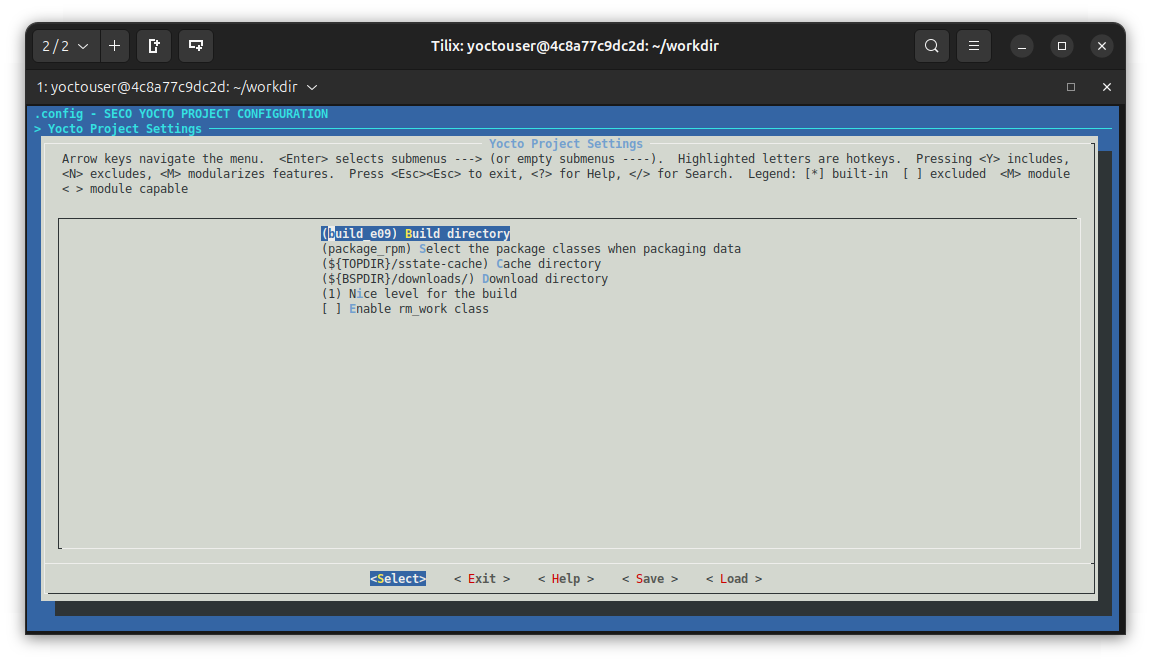 to the customized:
to the customized:
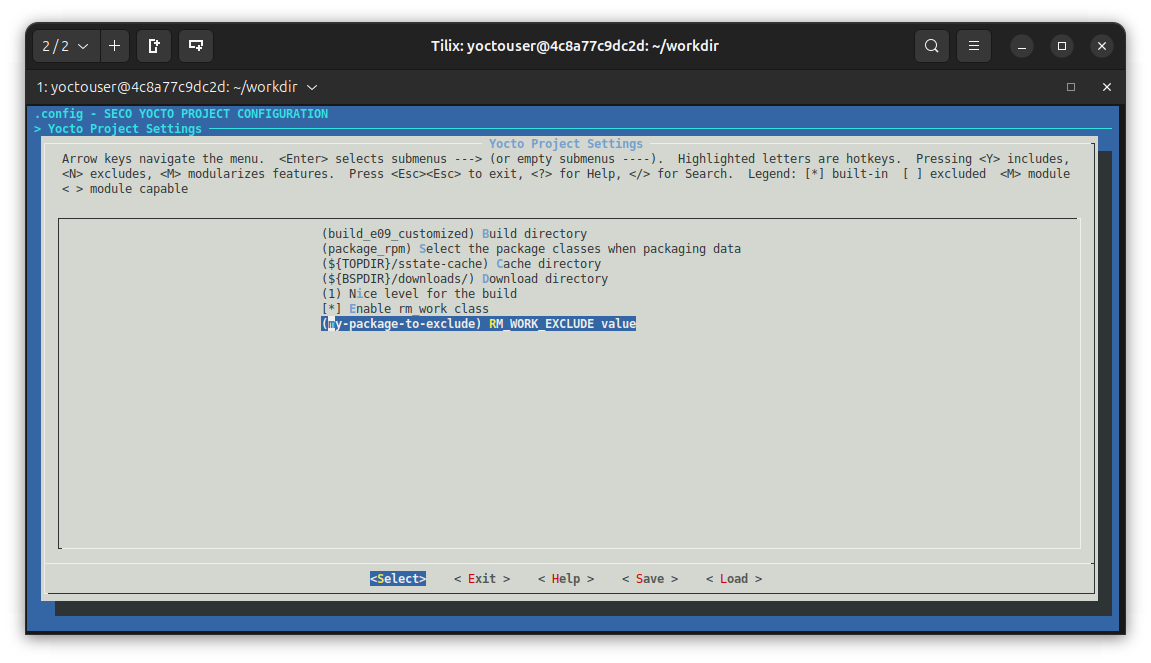
Once the configuration is customized save it as .config. Comparing the .config files before and after the customization results in:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir$ diff .config-orig .config
31c31
< CONFIG_ES_BUILD-DIR="build_e09"
---
> CONFIG_ES_BUILD-DIR="build_e09_customized"
36c36,37
< # CONFIG_YS-APPEND_INHERIT_rm_work is not set
---
> CONFIG_YS-APPEND_INHERIT_rm_work=y
> CONFIG_YS-APPEND_RM-WORK-EXCLUDE="my-package-to-exclude"
Then to create the build environment with the selected changes, run normally:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh -c
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-URL found in the configuration.
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-REALM found in the configuration.
WARNING: no CONFIG_CLOUD_ASTARTE-PAIRING-TOKEN found in the configuration.
WARNING: no RAUC found in the configuration.
Welcome to SECO BSP
The Yocto Project has extensive documentation about OE including a
reference manual which can be found at:
http://yoctoproject.org/documentation
For more information about OpenEmbedded see their website:
http://www.openembedded.org/
Your build environment has been configured with:
MACHINE=seco-rk3568-e09
SDKMACHINE=i686
DISTRO=clea-os-fb
EULA=
As a confirm check the path of the build directory and search into conf/local.conf the variable added with menuconfig:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$ pwd
/home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09_customized
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$ cat conf/local.conf | grep -E '^INHERIT|^RM_WORK_EXCLUDE'
INHERIT += "rm_work"
RM_WORK_EXCLUDE += "my-package-to-exclude"
Reconfigure an already existing project
Assuming that an already existing build directory needs to be reconfigured, firstly re-create the environment with:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh <build_directory>
then reconfigure the project with:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir/<build_directory>$ . ./seco-setup.sh -r
and the menuconfig landing page will appear, similarly as when customizing the configuration before creating the build directory. Running this command causes:
- opening of
menuconfigto edit the configuration. - save the former
confdirectory into an archive named<build-dir-name>_conf_backup_<date>_<time>.tar.gz. - renew the content of
confwith the new changes.
For example, using the directory build_e09_customized described in the previous section:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir$ . ./seco-setup.sh build_e09_customized/
Welcome to SECO BSP
The Yocto Project has extensive documentation about OE including a
reference manual which can be found at:
http://yoctoproject.org/documentation
For more information about OpenEmbedded see their website:
http://www.openembedded.org/
Your configuration files at /home/yoctouser/workdir/build_e09_customized have not been touched.
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$
Open menuconfig with:
yoctouser@5088c7f89b1e:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$ . ./seco-setup.sh -r
and editing the configuration deselecting "Enable rm_work class" with:
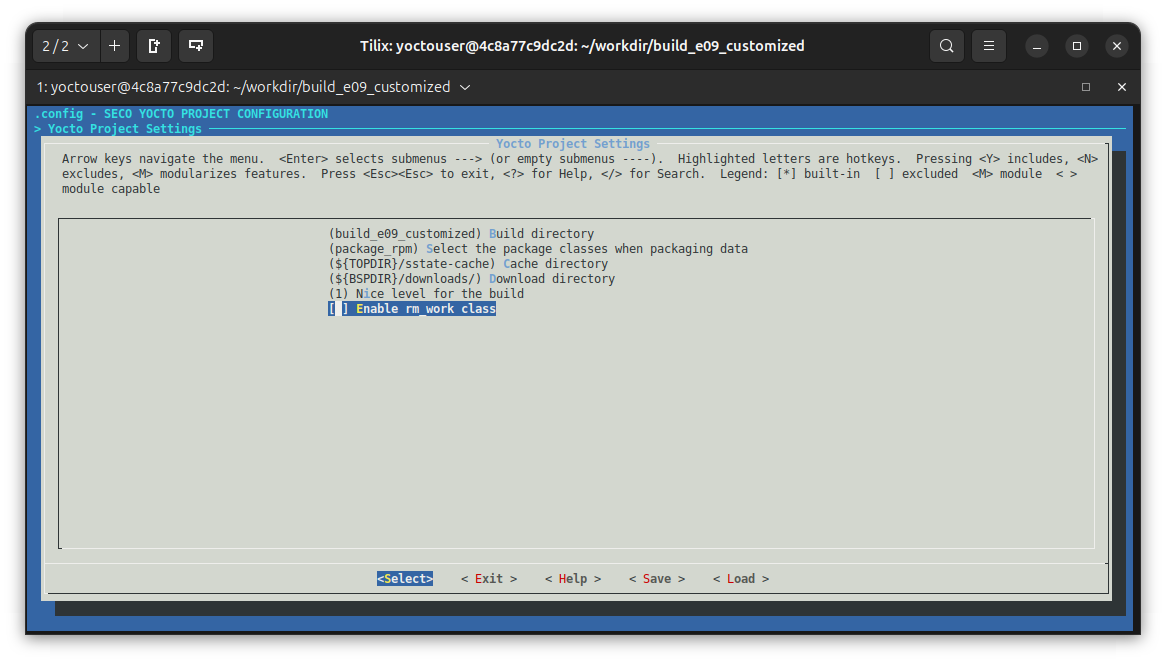
will remove from conf/local.conf the variables INHERITand RM_WORK_EXCLUDE:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$ cat conf/local.conf | grep -E '^INHERIT|^RM_WORK_EXCLUDE'
The former conf directory is saved in build_e09_customized with the archive build_e09_customized_conf_backup_20241211_150814.tar.gz:
yoctouser@4c8a77c9dc2d:~/workdir/build_e09_customized$ ll
total 20
drwxrwxr-x 3 yoctouser yoctouser 4096 Dec 11 15:22 ./
drwx------ 7 yoctouser yoctouser 4096 Dec 11 14:51 ../
-rw-rw-r-- 1 yoctouser yoctouser 6444 Dec 11 15:08 build_e09_customized_conf_backup_20241211_150814.tar.gz
drwxrwxr-x 2 yoctouser yoctouser 4096 Dec 11 15:08 conf/
lrwxrwxrwx 1 yoctouser yoctouser 49 Dec 11 14:39 seco-setup.sh -> /home/yoctouser/workdir/layers/base/seco-setup.sh*
NOTE: this is the only way to recongifure a project.
If the user runs the commands
. ./seco-setup.sh -mand. ./seco-setup.sh -cto reconfigure an already existing folder, if the build directory name is the same, then no changes will be applied as the folder already exists.